Introduction to Engineering Plastics: Features and Applications
06 July 2024
Introduction
Engineering plastics, also known as high performance plastics, are a category of materials specifically designed to offer superior mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties compared to regular plastics. As a result, engineering polymers have become an essential component in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electrical and electronics, healthcare, and more. This article provides a brief overview of the key characteristics, applications, benefits, and types of engineering plastics.
Key Features of Engineering Plastics
• High Mechanical Strength:
Engineering plastics, especially reinforced types, provide excellent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, impact resistance, and toughness.
• High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:
Despite being lightweight, engineering plastics exhibit high strength and rigidity, making them suitable for weight-sensitive applications such as aerospace and automotive industries.
• High Dimensional Stability:
Many engineering plastics can maintain their dimensional stability at high temperatures, which is crucial in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics where components are subjected to thermal stress.
• Good Chemical Resistance:
Engineering plastics are inherently resistant to chemicals such as acids and solvents, making them suitable for use in environments exposed to chemical substances, such as chemical processing plants.
• Excellent Electrical Insulation:
Many engineering plastics possess excellent electrical insulation properties, making them suitable for applications in the electrical and electronics industry.
• High Wear Resistance:
Some engineering plastics have low friction coefficients, making them suitable for applications requiring reduced friction, such as bearings and gears.
• Good Processability:
Engineering plastics can be easily processed using methods such as injection molding and extrusion, allowing designers to create innovative and complex parts.
Benefits of Engineering Plastics
Engineering plastics offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for many applications:
• Advanced Performance: Engineering plastics offer superior mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties compared to commodity polymers, improving performance and reliability in required applications.
• Cost-Effectiveness: Although engineering plastics may have higher initial costs than regular plastics, their longer lifespan, higher performance, and reduced maintenance requirements lead to long-term cost savings.
• Sustainability: Many engineering plastics are recyclable and can be recycled using environmentally friendly methods, making them a sustainable choice for eco-friendly industries.
• Versatility: Engineering plastics are available in a wide range of grades and formulations, allowing for customization to meet specific application requirements. This versatility enables engineers to tailor materials to their needs.
• Compliance with Regulations: Engineering plastics can be easily formulated to comply with safety, health, and environmental standards.
Applications of Engineering Plastics
Engineering plastics are used in a wide range of industries and sectors, including:
• Automotive Industry:
Due to their lightweight nature and high resistance to impact and corrosion, engineering plastics are widely used in automotive components such as interior trim, engine parts, and electrical connectors.
• Aerospace Industry:
Engineering plastics are used in interior decorations, structural components, and engine parts of aircraft due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, flame resistance, and dimensional stability.
• Electrical and Electronics:
Thanks to their excellent electrical insulation properties and flame resistance, engineering plastics serve as insulators and protective materials in electronic devices, ensuring electrical safety and thermal management.
• Medical Equipment:
Engineering plastics, known for their biocompatibility, sterilizability, and high chemical resistance, are extensively used in medical instruments and devices such as surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
• Consumer Goods:
With their durability, high aesthetic appeal, and ease of processing, engineering plastics find applications in consumer goods such as household appliances, sport goods, and packaging materials.
• Industrial Components:
Engineering plastics are utilized in various industrial equipment due to their high wear resistance, including gears, bearings, and other mechanical parts.
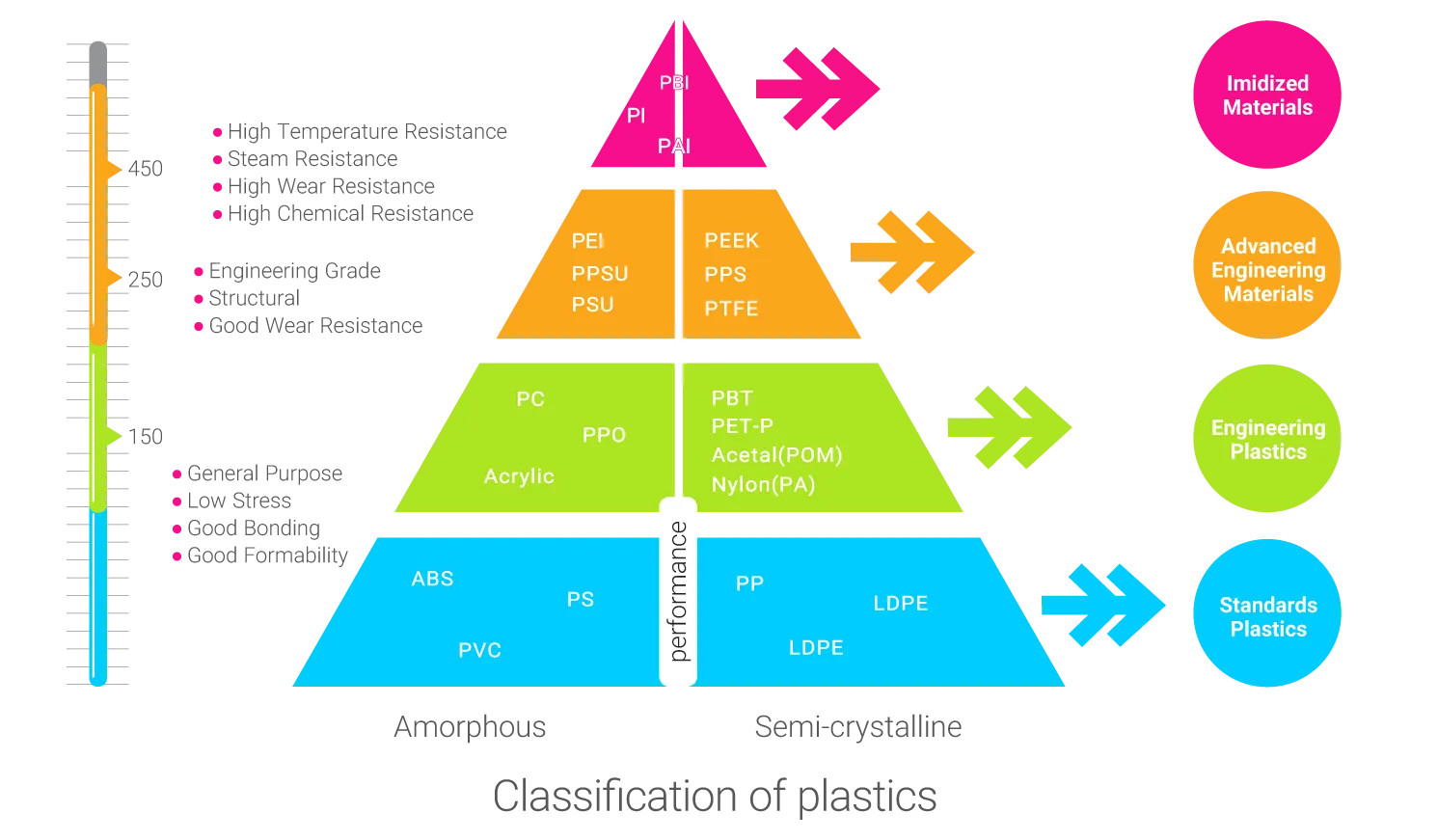
Types of Engineering Plastics
There are various types of engineering plastics, each with its own set of unique properties and applications. Some types of engineering plastics include:
• Polyamide (PA):
Polyamide, also known as nylon, is widely used in gears, bearings, and automotive parts due to its low density, high tensile strength, excellent resistance to wear and impact, and good machinability.
• Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET):
PET is often used in beverage bottles and food containers due to its transparency, good chemical resistance, and ease of processing.
• Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT):
PBT finds extensive applications in automotive and electrical industries due to its excellent insulating properties and high heat resistance.
• Polycarbonate (PC):
PC is ideal for applications such as automotive glazing, eyewear, and electronic displays due to its exceptional impact resistance and high optical clarity.
• Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS):
ABS is a suitable choice for consumer goods like toys and automotive trim parts due to its good impact resistance and easy moldability.
• Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO):
PPO demonstrates high tensile and impact strength, great dimensional stability and exceptional resistance to water and steam. PPO is used for automotive fenders, electronics housings, and medical instruments.
• Polytetrafluroethylene (PTFE):
PTFE exhibits very high working temperatures, low moisture absorption, low coefficient of friction and high chemical resistance. PTFE is used in many different applications, such as wiper blades, cookware, pipes, medical instruments and more.
• Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK):
PEEK is a thermoplastic with exceptional mechanical and chemical properties, making it widely used in aerospace and medical industries.
• Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS):
PPS is highly resistant to chemicals and heat, making it suitable for automotive parts, electrical connectors, and industrial components.
• Polyetherimide (PEI):
PEI is utilized in aerospace, automotive, and electronic industries for its high temperature resistance and excellent dimensional stability.
Summery
Today, engineering plastics offer a superior combination of mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical properties along with flexibility in design and cost-effectiveness. They have become the preferred choice for a wide range of industries, from automotive and aerospace to electronics and medical devices. Parsa Polymer Sharif offers engineering blends in two families: ParsaAmid based on PA (PA6, PA66, and PA6/PA66 blends) and ParsaNova based on polymers such as PC, ABS, PBT, and PET, as well as alloys such as PC/ABS, PBT/PET, and PC/PBT, catering to a diverse range of applications. These blends, reinforced with glass fibers, mineral fillers, flame retardants, impact modifiers, and UV stabilizers, are suitable for all manufacturing processes including injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding.
References
1. https://www.xometry.com/resources/materials/all-about-engineering-plastics/
2. https://steelcal.com/engineering-plastics-versatile-materials-shaping-the-modern-world/
3. https://sungplastic.com/engineering-plastics-a-comprehensive-guide-to-properties-applications-and-modified/